Portal:Society
The Society Portal
A society (/səˈsaɪəti/) is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Societies are characterized by patterns of relationships (social relations) between individuals who share a distinctive culture and institutions; a given society may be described as the sum total of such relationships among its constituent members.
Human social structures are complex and highly cooperative, featuring the specialization of labor via social roles. Societies construct roles and other patterns of behavior by deeming certain actions or concepts acceptable or unacceptable—these expectations around behavior within a given society are known as societal norms. So far as it is collaborative, a society can enable its members to benefit in ways that would otherwise be difficult on an individual basis.
Societies vary based on level of technology and type of economic activity. Larger societies with larger food surpluses often exhibit stratification or dominance patterns. Societies can have many different forms of government, various ways of understanding kinship, and different gender roles. Human behavior varies immensely between different societies; humans shape society, but society in turn shapes human beings. (Full article...)
Selected article
Featured picture
A Punch cartoon from 17 June 1876 showing Russia preparing to let slip "the dogs of war", its imminent engagement in the growing conflict between Slavic states in the Balkans and Turkey, while policeman John Bull (representing Britain) warns Russia to take care. The Slavic states of Serbia and Montenegro would declare war on Turkey at the end of June, and Russia formally joined the war in April 1877.
Did you know...
- ... that after the American Civil War ended, Ladies' Memorial Associations sprang up all over the South to bury Johnny Reb, build monuments (example pictured) in honor of Confederate soldiers, and propagate the Lost Cause?
- ... that Body of Proof episode "Society Hill" marked the first appearance of Megan Hunt's mother Joan, played by Six Feet Under star Joanna Cassidy?
- ... that Bernhard Kummer regarded the conversion of the Germanic peoples as a cultural catastrophe and thus titled his doctoral thesis Midgards Untergang?
Anniversaries this month
- 1 May 1776 - Foundation of the Bavarian Illuminati, an Enlightenment-era secret society
- 1 May 1869 - New York Genealogical and Biographical Society elects its first woman member
- 7 May 1964 - U.S. President Lyndon B. Johnson (pictured) first makes reference to the Great Society
- 10 May 1793 - Society of Revolutionary Republican Women officially registered at the Paris Commune
Selected quote
Selected biography
Featured audio
Categories

|
Category Fictional society not found
Category Corporate groups not found
|
Category Philosophy and society not found
Category Wikipedia books on society not found
|
Related portals
Recognized content
Featured articles
 2012 phenomenon
2012 phenomenon Archaeology, Anthropology, and Interstellar Communication
Archaeology, Anthropology, and Interstellar Communication 1689 Boston revolt
1689 Boston revolt Communication
Communication 1969 Curaçao uprising
1969 Curaçao uprising Diocletianic Persecution
Diocletianic Persecution W. E. B. Du Bois
W. E. B. Du Bois Female genital mutilation
Female genital mutilation First homosexual movement
First homosexual movement From the Doctor to My Son Thomas
From the Doctor to My Son Thomas Fuck (2005 film)
Fuck (2005 film) Fuck: Word Taboo and Protecting Our First Amendment Liberties
Fuck: Word Taboo and Protecting Our First Amendment Liberties Growing Up Absurd
Growing Up Absurd Homo antecessor
Homo antecessor 1981 Irish hunger strike
1981 Irish hunger strike Theodora Kroeber
Theodora Kroeber Solo Man
Solo Man Rosewood massacre
Rosewood massacre Stonewall riots
Stonewall riots George Washington and slavery
George Washington and slavery
Featured lists
Good articles
 1950s American automobile culture
1950s American automobile culture Timeline of the Egyptian revolution of 2011
Timeline of the Egyptian revolution of 2011 Agriculture
Agriculture Alfred Kroeber: A Personal Configuration
Alfred Kroeber: A Personal Configuration Algorithmic bias
Algorithmic bias America's 60 Families
America's 60 Families Anarchism
Anarchism Anarchism in Cuba
Anarchism in Cuba Anonymous (hacker group)
Anonymous (hacker group) Anti-nuclear movement in Australia
Anti-nuclear movement in Australia Anna Apostolaki
Anna Apostolaki Archaeoastronomy
Archaeoastronomy The Archives of the Planet
The Archives of the Planet Aroused (film)
Aroused (film) 2008 attacks on Christians in southern Karnataka
2008 attacks on Christians in southern Karnataka Australopithecus africanus
Australopithecus africanus Australopithecus afarensis
Australopithecus afarensis Australopithecus bahrelghazali
Australopithecus bahrelghazali Australopithecus deyiremeda
Australopithecus deyiremeda Australopithecus garhi
Australopithecus garhi Australopithecus sediba
Australopithecus sediba Balangoda Man
Balangoda Man Before the Dawn (Wade book)
Before the Dawn (Wade book) Birth control
Birth control Black Lives Matter
Black Lives Matter Boerehaat
Boerehaat The Bog People
The Bog People Bomis
Bomis Boston Massacre
Boston Massacre Catilinarian conspiracy
Catilinarian conspiracy Cueva de las Manos
Cueva de las Manos Celebrity Studies
Celebrity Studies Chakh Akhriev
Chakh Akhriev Child prostitution
Child prostitution History of Christian thought on persecution and tolerance
History of Christian thought on persecution and tolerance A Community of Witches
A Community of Witches Compulsory Miseducation
Compulsory Miseducation Criminalization of homosexuality
Criminalization of homosexuality Cro-Magnon
Cro-Magnon Cult film
Cult film Culture of the Song dynasty
Culture of the Song dynasty Cutting the Mustard
Cutting the Mustard Hilda Ellis Davidson
Hilda Ellis Davidson Demographic history of Scotland
Demographic history of Scotland Demographics of the Supreme Court of the United States
Demographics of the Supreme Court of the United States Denisovan
Denisovan Deus Ex: Human Revolution
Deus Ex: Human Revolution Diaphoneme
Diaphoneme Diver communications
Diver communications Dmanisi hominins
Dmanisi hominins Domestication
Domestication Double burden
Double burden Dreamtime (book)
Dreamtime (book) Émile Durkheim
Émile Durkheim EST and The Forum in popular culture
EST and The Forum in popular culture Education
Education Ely and Littleport riots of 1816
Ely and Littleport riots of 1816 Extremely online
Extremely online Family in the United States
Family in the United States Feminism
Feminism Feminist economics
Feminist economics The finger
The finger Forensic anthropology
Forensic anthropology Free Expression Policy Project
Free Expression Policy Project Stephen Fuchs
Stephen Fuchs Future of Families and Child Wellbeing Study
Future of Families and Child Wellbeing Study Gender and sexual minorities in the Ottoman Empire
Gender and sexual minorities in the Ottoman Empire Genetically modified organism
Genetically modified organism Anca Giurchescu
Anca Giurchescu God's Choice
God's Choice Erving Goffman
Erving Goffman Paul Goodman
Paul Goodman Herto Man
Herto Man Historiography of the Crusades
Historiography of the Crusades History of agriculture
History of agriculture Hitachi Magic Wand
Hitachi Magic Wand Winifred Hoernlé
Winifred Hoernlé Homo rudolfensis
Homo rudolfensis Homo ergaster
Homo ergaster Homo habilis
Homo habilis Homo heidelbergensis
Homo heidelbergensis Homo longi
Homo longi Homo luzonensis
Homo luzonensis Homo naledi
Homo naledi Hooray Henry
Hooray Henry Human
Human Human interactions with insects
Human interactions with insects I Ching
I Ching Globalization and women in China
Globalization and women in China Incel
Incel Ivatan people
Ivatan people 1968–1969 Japanese university protests
1968–1969 Japanese university protests Java Man
Java Man Jewellery of the Berber cultures
Jewellery of the Berber cultures Joint custody (United States)
Joint custody (United States) Kenyanthropus
Kenyanthropus Kirkbride Plan
Kirkbride Plan LGBT and Wikipedia
LGBT and Wikipedia Language
Language Lantian Man
Lantian Man Ralph Larkin
Ralph Larkin Lesbian
Lesbian Luttra Woman
Luttra Woman Magic, Witchcraft and the Otherworld
Magic, Witchcraft and the Otherworld Bronisław Malinowski
Bronisław Malinowski The Man-Eating Myth
The Man-Eating Myth Man of the Hole
Man of the Hole March for Our Lives Portland
March for Our Lives Portland March for Science Portland
March for Science Portland March of loyalty to martyrs
March of loyalty to martyrs Karl Marx
Karl Marx Josef Mengele
Josef Mengele Maria Mies
Maria Mies Misanthropy
Misanthropy Models of communication
Models of communication A More Perfect Union: Advancing New American Rights
A More Perfect Union: Advancing New American Rights Mork Goes Erk
Mork Goes Erk Mountain Meadows Massacre
Mountain Meadows Massacre Myth of the clean Wehrmacht
Myth of the clean Wehrmacht Native American mascot controversy
Native American mascot controversy Neanderthal
Neanderthal The Neanderthals Rediscovered
The Neanderthals Rediscovered New World Order (conspiracy theory)
New World Order (conspiracy theory) No Lifeguard on Duty
No Lifeguard on Duty Not My Presidents Day
Not My Presidents Day Not in Front of the Children
Not in Front of the Children Nudity
Nudity Observations Made During a Voyage Round the World
Observations Made During a Voyage Round the World On the Internet, nobody knows you're a dog
On the Internet, nobody knows you're a dog Otaku
Otaku Ovulatory shift hypothesis
Ovulatory shift hypothesis Paranthropus
Paranthropus Paranthropus aethiopicus
Paranthropus aethiopicus Paranthropus boisei
Paranthropus boisei Paranthropus robustus
Paranthropus robustus Peking Man
Peking Man Political party
Political party Polyethnicity
Polyethnicity Positioning theory
Positioning theory Potential cultural impact of extraterrestrial contact
Potential cultural impact of extraterrestrial contact 1956 Poznań protests
1956 Poznań protests Protests in Canada against the Sri Lankan Civil War
Protests in Canada against the Sri Lankan Civil War Proto-globalization
Proto-globalization Psychedelic music
Psychedelic music Iveta Radičová
Iveta Radičová Rally to Restore Sanity and/or Fear
Rally to Restore Sanity and/or Fear Aparna Rao
Aparna Rao A Rape on Campus
A Rape on Campus Reborn doll
Reborn doll Herbert Hope Risley
Herbert Hope Risley The Road to Total Freedom
The Road to Total Freedom Romania in the Early Middle Ages
Romania in the Early Middle Ages Rose Street Club
Rose Street Club Royal intermarriage
Royal intermarriage Edward Said
Edward Said Schramm's model of communication
Schramm's model of communication Sex, Sin, and Blasphemy
Sex, Sin, and Blasphemy Sheng nü
Sheng nü Silver
Silver Simele massacre
Simele massacre Maria Simon (sociologist)
Maria Simon (sociologist) Kateryna Skarzhynska
Kateryna Skarzhynska Slavery in Haiti
Slavery in Haiti Social identity theory
Social identity theory Society
Society Sociology of leisure
Sociology of leisure Source–message–channel–receiver model of communication
Source–message–channel–receiver model of communication Stay-at-home dad
Stay-at-home dad Stratford Dialectical and Radical Club
Stratford Dialectical and Radical Club Tautavel Man
Tautavel Man Team effectiveness
Team effectiveness Tefillin
Tefillin Think of the children
Think of the children Trance and Dance in Bali
Trance and Dance in Bali Truce term
Truce term Max Weber
Max Weber Weiquan movement
Weiquan movement Whiskey Rebellion
Whiskey Rebellion Who We Are and How We Got Here
Who We Are and How We Got Here Benjamin Lee Whorf
Benjamin Lee Whorf Witch-hunts in India
Witch-hunts in India Women's March on Portland
Women's March on Portland Yuanmou Man
Yuanmou Man Yuri (genre)
Yuri (genre) Florian Znaniecki
Florian Znaniecki
Featured pictures
-
20151030 Syrians and Iraq refugees arrive at Skala Sykamias Lesvos Greece 2
-
Bertillon, Alphonse, fiche anthropométrique recto-verso
-
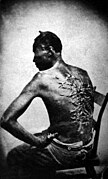
Cicatrices de flagellation sur un esclave
-
Daisy (1964)
-
DurbanSign1989
-
Frances Benjamin Johnston, Self-Portrait (as "New Woman"), 1896
-
Jane Addams - Bain News Service
-
Marine da nang
-
Nanook of the North
-
SantaCruz-CuevaManos-P2210651b
-
United States President Barack Obama bends down to allow the son of a White House staff member to touch his head
-
W.E.B. Du Bois by James E. Purdy, 1907
-
Xiahe mandible
Things you can do
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
WikiProjects
Web resources
- Definition of Society from the OED.
- Internet Modern History Sourcebook: Industrial Revolution
- "The Day the World Took Off" Six part video series from the University of Cambridge tracing the question "Why did the Industrial Revolution begin when and where it did."
- BBC History Home Page – Industrial Revolution
- National Museum of Science and Industry website – machines and personalities
- Industrial Revolution and the Standard of Living by Clark Nardinelli - the debate over whether standards of living rose or fell.