Portal:Energy
| Main page | New articles & Tasks |
 The Energy Portal Welcome to Wikipedia's Energy portal, your gateway to energy. This portal is aimed at giving you access to all energy related topics in all of its forms.
|
Page contents: Selected article • Selected image • Selected biography • Did you know? • General images • Quotations • Related portals • Wikiprojects • Major topics • Categories • Help • Associated Wikimedia |
Introduction
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek ἐνέργεια (enérgeia) 'activity') is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J).
Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy.
Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass when stationary (called rest mass) also has an equivalent amount of energy whose form is called rest energy, and any additional energy (of any form) acquired by the object above that rest energy will increase the object's total mass just as it increases its total energy.
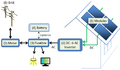
Human civilization requires energy to function, which it gets from energy resources such as fossil fuels, nuclear fuel, or renewable energy. The Earth's climate and ecosystems processes are driven by the energy the planet receives from the Sun (although a small amount is also contributed by geothermal energy). (Full article...)
Selected article
Deposits of oil shale occur around the world, including major deposits in the United States of America. Estimates of global deposits range from 2.8 trillion to 3.3 trillion barrels (450×109 to 520×109 m3) of recoverable oil.
The chemical process of pyrolysis can convert the kerogen in oil shale into synthetic crude oil. Heating oil shale to a sufficiently high temperature will drive off a vapor which processing can distill (retort) to yield a petroleum-like shale oil—a form of unconventional oil—and combustible oil-shale gas (the term shale gas can also refer to gas occurring naturally in shales). Industry can also burn oil shale directly as a low-grade fuel for power generation and heating purposes and can use it as a raw material in chemical and construction-materials processing.
Oil shale has gained attention as an energy resource as the price of conventional sources of petroleum has risen and as a way for some areas to secure independence from external suppliers of energy. At the same time, oil-shale mining and processing involve a number of environmental issues, such as land use, waste disposal, water use, waste-water management, greenhouse-gas emissions and air pollution. Estonia and China have well-established oil shale industries, and Brazil, Germany, Israel and Russia also utilize oil shale.
Selected image

Photo credit: Postdlf
Lightning is a highly visible form of energy transfer.
Did you know?
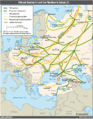
- During World War I, the German Army produced shale oil from Yarmouk oil shale deposits in Jordan to operate the Hijazi Railway (pictured)?
- Dennis Spurgeon, formerly chief operating officer at uranium supplier USEC Inc., became the United States Assistant Secretary for Nuclear Energy in 2006?
- Japan Canada Oil Sands Limited was the first offshore oil company to exploit the Athabasca oil sands in Canada?
- Teesside Power Station is the largest combined-cycle gas turbine (CCGT) plant in Europe.?
- The Klaipėda Geothermal Demonstration Plant in Lithuania was the first geothermal plant in the Baltic Sea region?
- Hitachi Zosen Corporation built the first oil tanker in Japan in 1908 per an order by Standard Oil Company?
- Coalbed methane is a form of natural gas extracted from coal beds?
- When constructed in 1906, the Baku–Batumi pipeline was the world's longest kerosene pipeline?
Selected biography
Rockefeller founded the Standard Oil Company in 1870 and ran it until he retired in the late 1890s. He continued to retain his stock and his title as president until 1911, when the company was broken up for carrying out illegal monopoly practices. The new companies formed included the predecessors of Conoco, Amoco, Chevron, Esso, Mobil and Sohio. Rockefeller, who had rarely sold shares, owned stock in all of them. As gasoline had grown in importance his wealth had soared and he became the world's richest man and the first billionaire.
Rockefeller's fortune was used to create the modern systematic approach of targeted philanthropy with foundations that had a major impact on medicine, education, and scientific research. His foundations pioneered the development of medical research, and was instrumental in the eradication of hookworm and yellow fever. At his death, at the age of 98, Rockefeller's remaining fortune was estimated at $1.4 billion. As a percentage of the United States economy, no other American fortune has ever come close.
General images
Quotations
- "In recent years, new nations have entered enthusiastically into industrial production, thereby increasing their energy needs. This has led to an unprecedented race for available resources. Meanwhile, some parts of the planet remain backward and development is effectively blocked, partly because of the rise in energy prices. What will happen to those peoples?" – Pope Benedict XVI, 2007
- "In order to prevent the harmful consequences that crude oil price volatility is having on the well-being of our people, it is urgent that we convene a World Leaders Summit to present alternative solutions to this serious problem, which could quite possibly be a significant shock to the prosperity of developing nations." – Leonel Fernández, 2005
Related portals
WikiProjects
WikiProjects connected with energy:
Other WikiProjects that may be of interest:
Major topics
Major categories
National energy supply, use & conservation
National electricity sector
Politics, economics, environment
- Climate change
- Energy conservation
- Energy economics
- Energy crises
- Energy development
- Energy policy
- Peak oil
Energy sources
- Fuels
- Biofuels
- Fossil fuels
- Fusion power
- Nuclear technology
- Renewable energy
- Energy conversion
- Electric power
- Energy storage
Energy-related design
Scientific usage
Help

Puzzled by energy?
Can't answer your question?
Don't understand the answer?
- Ask at the reference desk
- Read the Wikipedia help pages
For further ideas, to leave a comment, or to learn how you can help improve and update this portal, see the talk page.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus